Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ ( 1 x^2 ) dy/dx y = e^tan 1xGet answer Solve (x1) dy,dx ny = e^(x) (x1) ^(n1) Apne doubts clear karein ab Whatsapp par bhi Try it nowCalculus Find dy/dx y=1/ (x^2) y = 1 x2 y = 1 x 2 Differentiate both sides of the equation d dx (y) = d dx ( 1 x2) d d x ( y) = d d x ( 1 x 2) The derivative of y y with respect to x x is y' y ′ y' y ′ Differentiate the right side of the equation Tap for more steps
What Is The Solution For The Differential Equation Math Tan 1 X Y Dx 1 X 2 Dy Math Quora
(1+x^2)dy/dx+y=e^tan^-1x
(1+x^2)dy/dx+y=e^tan^-1x-Get answer Solve `(1x^2) dy/dxy=e^(tan^1x)` This browser does not support the video element3 If √y = cos − 1x, then it satisfies the differential equation (1 − x2) − xdy dx = c, where c is equal to WBJEE 14 4 The curve y = (cosx y)1 / 2 satisfies the differential equation WBJEE 14 5 A solution of the differential equation (dy dx)2 − xdy dx y = 0 is AMU 13




Solve The Differential Equations In Exercises 1 14 Chegg Com
Get answer Solve `(1x^2) dy/dxy=e^(tan^1x)` Step by step solution by experts to help you in doubt clearance & scoring excellent marks in exams Y = e^tan^1x prove that (1x^2)d^2y/dx^2 (2x1)dy/dx iamspandan is waiting for your help Add your answer and earn points Rewriting the given diff eqn (DE) as #dy/dxy=2x#, we find that it is a linear DE of the form #dy/dxyP(x)=q(x)# To find its gen soln (GS), we need to multiply it by the integrating factor (IF) #e^(intP(x)dx# Since, #P(x)=1, intP(x)dx=int1dx=x " IF is "e^x# Multiplying the DE by IF, we get, #e^xdy/dxye^x=2xe^x#
Calculus is the association of change in one variable with respect to another So dy/dx literally means how the variable y changes as x changes Imagine a graph, draw the line y = 1 It doesn't matter what value of x you look at, y = 1 It x changes, decreases or increaes, y will always be 1Share It On Facebook Twitter Email 1 Answer 1 vote answered by Jay01 (395k points) selected by Abhilasha01 Best answer The given differential equation isFind the equation of a curve passing through origin and satisfying the differential equation (1x^2)dy/dx 2xy = 4x^2 asked in Mathematics by AsutoshSahni (526k points) differential equations;
So we use the integrating factor method 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 = ((1 𝑦^2))/(tan^(−1) y − x) This is not of the form 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥𝑃𝑦=𝑄 ∴ We need to find 𝑑𝑥/𝑑𝑦 𝑑𝑥/𝑑𝑦 = (tan^(−1)𝑦 − 𝑥)/(1 𝑦^2 ) 𝑑𝑥/𝑑𝑦 = tan^(−1)𝑦/(1 𝑦^2 ) − 𝑥/(1 𝑦^2 ) 𝑑𝑥/𝑑𝑦 𝑥/(1 𝑦^2 ) − (tan^(−1)𝑦 )/(1B Tech,BE,BSc MathematicsSolve (1x^2)dy/dxxy=ax Solve (1 x 2)(dy/dx) y = e tan^–1 x differential equations;



Www Math Tamu Edu Irinaholmes M308f M308f Hw3 Sol Pdf




If Y Ex Tan 1 X Prove That 1 X2 D2y Dx2 2 1 X X2 Dy Dx 1 X 2 Y 0 Maths Continuity And Differentiability Meritnation Com
Note now that sec2(x − y) = 1 tan2(x − y) = 1 y2 (1 x2)2 so dy dx = 1 y2 (1x2)2 2xy (1x2)2 1 y2 (1x2)2 1 1x2 and multiplying numerator and denominator by (1 x2)2 dy dx = (1 x2)2 y2 2xy (1 x2)2 y2 1 x2 dy dx = x4 2x2 y2 2xy 1 x4 3x2 y2 2 Answer linkSolve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more2xydxx2dy=0 Three solutions were found d = 0 y = 0 x = 0 Step by step solution Step 1 Equation at the end of step 1 3x2yd = 0 Step 2 Solving a Single Variable Equation What is the solution of the differential equation ydx (xx^2y)dy=0



1




The Solution Of Differential Equation 1 X 2 Dy Dx
Calculus Find dy/dx y=1/x y = 1 x y = 1 x Differentiate both sides of the equation d dx (y) = d dx ( 1 x) d d x ( y) = d d x ( 1 x) The derivative of y y with respect to x x is y' y ′ y' y ′ Differentiate the right side of the equation Tap for more steps The solution of `(1x^(2))(dy)/(dx)y=e^(tan^1x)`, is given byRelated Documents Complex Numbers Complex numbers are used in alternating current theory and in mechanical vector analysis;




If Y Tan 1 X 2 Prove That 1 X2 2y2 2x 1 X2 Y1 2 Explain In Great Detail Mathematics Topperlearning Com Z68xug




If Y Tan 1x 2 Show That X 2 1 2y2 2x X 2 1 2
TruongSon N I seem to recall my professor forgetting how to deriving this This is what I showed him y = arctanx tany = x sec2y dy dx = 1 dy dx = 1 sec2y Since tany = x 1 and √12 x2 = √1 x2, sec2y = ( √1 x2 1)2 = 1 x2Get answer Solve (dy),(dx)=(1y^2),(1x^2) Apne doubts clear karein ab Whatsapp par bhi Try it nowGet answer Solve the equation (1x^2)tan^1x*(dy),(dx)y=0 Apne doubts clear karein ab Whatsapp par bhi Try it now




Solve The Differential Equations In Exercises 1 14 Chegg Com
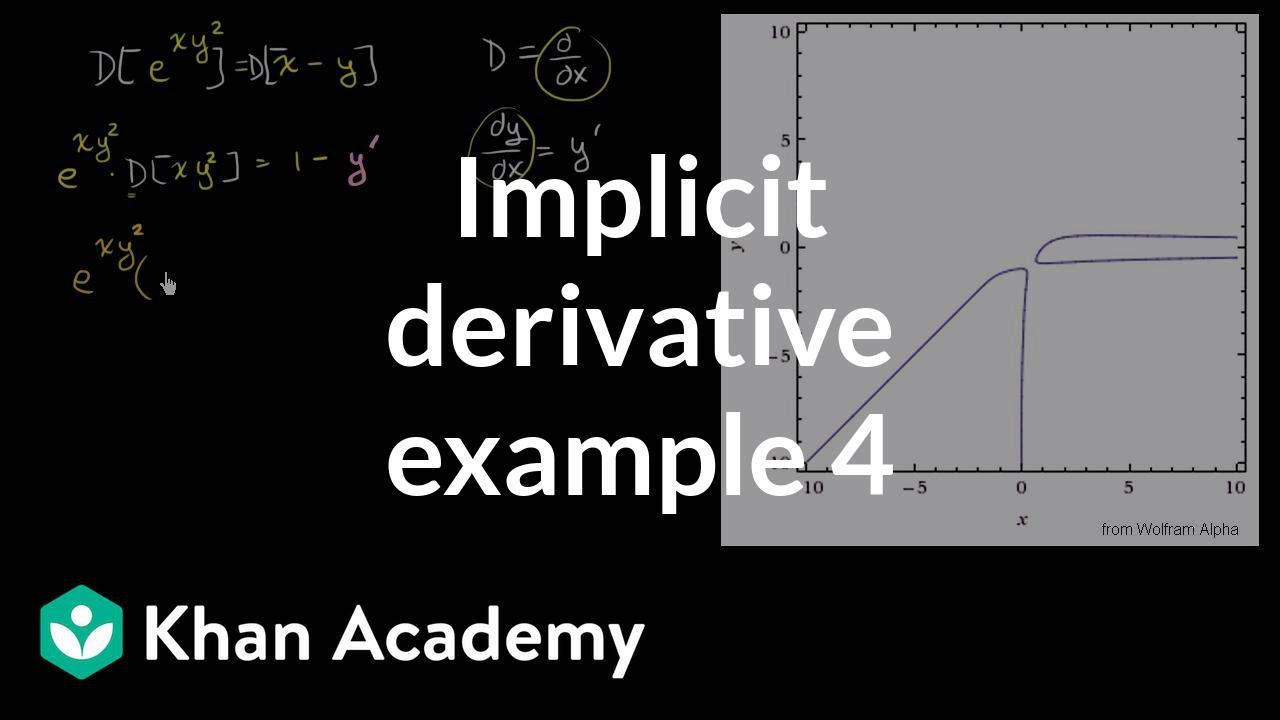



Implicit Differentiation Advanced Example Video Khan Academy
As WW1 pointed before, make d t d v = d x d v d t d x = d x d v v = k (1 3 x 2) Now, you have a separable differential equation that you can solve easily integrating ∫ v d v = ∫ k (1 x 2),For each of the differential equations given in exercise 1 to 1 2,find the general solution 1 d x d y 2 y = sin x 2 d x d y 3 y = e − 2 x 3 d x d y x y = x 2 4 d x d y sec= tan x (0 ≤ x ≤ 2 π ) 5 cos 2 x d x d y y = tan x (0 ≤ x ≤ 2 π0 votes 1 answer
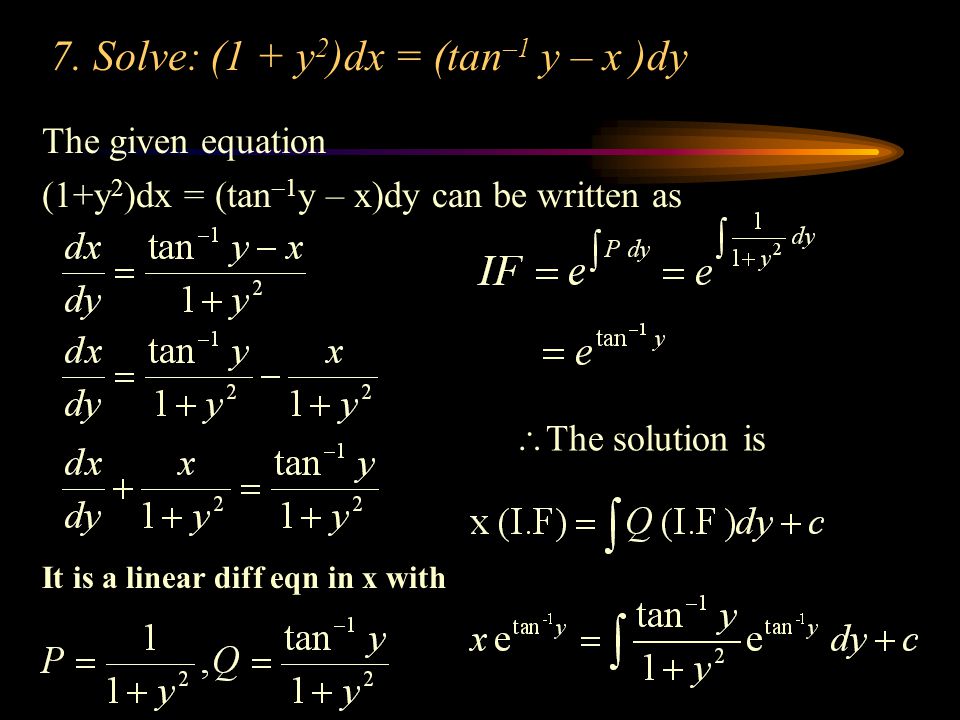



Differential Equations Ppt Video Online Download



Silo Tips Download 300 32 X I
SolutionShow Solution ` (1 x2) dy/dxy=e^ (tan^ (−1))x` `=>dy/dxy/ (1x^2)=e^ (tan^ (−1)x)/ (1x^2)` Comparing it with the standard equation, f'(x)yP=Q Now, integrating factor, `IF = e^Do you actually mean derivatives for matht/math?Differentiate using the Power Rule which states that d d x x n d d x x n is n x n − 1 n x n 1 where n = 2 n = 2 Multiply 2 2 by − 1 1 Reform the equation by setting the left side equal to the right side Reorder factors in −2e−x2 x 2 e x 2 x Replace y' y ′ with dy dx d y d x



Users Math Msu Edu Users Magyarp Math133 6 3 Natural Exp Fcn Pdf




For Problems 26 Determine An Integrating Factor Chegg Com
In calculus, Leibniz's notation, named in honor of the 17thcentury German philosopher and mathematician Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, uses the symbols dx and dy to represent infinitely small (or infinitesimal) increments of x and y, respectively, just as Δx and Δy represent finite increments of x and y, respectively Consider y as a function of a variable x, or y = f(x) We are asked to solve the differential equation (x − y) dy dx = x 2y We rearrange a little dy dx = x 2y x −y dy dx = 1 2(y x) 1 − (y x) (I) While I may not need to mention this, this differential equation is what is called a homogeneous differential equation I'llGiven y = (1 x 2) tan 1 x – x Differentiate wrtx dy/dx = (1 x 2) d/dx tan 1 x 2x tan 1 x – 1 = (1 x 2) ×1/ (1 x 2) 2x tan 1 x – 1 = 1 2x tan 1 x – 1 = 2x tan 1



Solve The Following Differential Equation 1 X 2 Dy Dx Y Tan 1x Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



Solve The Following Differential Equation 1 X 2 Dy Dx Y Tan 1x Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
Answer 3 on a question (1x^2)dy/dx y= e^tan1x the answers to smartanswersincom Find the differential dy when x=2 and dx=04Find the differential dy when x=2 and dx=08 2 Educator answers eNotescom will help you with any book or any questionBecause math\frac{dy}{dx}/math means derivative for mathx/math and if it is math\frac{dy}{dx}/math




Engineering Mathematics Notes




3 31 Class Work 4 Ye In X E D Y Tanx Y Homeworklib
Dy/dx = a / (x (x 2 a 2) 1/2) Sponsored Links Related Topics Mathematics Mathematical rules and laws numbers, areas, volumes, exponents, trigonometric functions and more ;Answer to Solve the initial value problem dy/dx = (y^2 1)/(x^2 1), y(2) = 2 By signing up, you'll get thousands of stepbystep solutions to I'll start with the second one for you Take the natural logarithm of both sides Now for the second I would differentiate term by term Let t = xy and u = yx Then lnt = ln(xy) and lnu = ln(yx) It follows that 1 t = dy dx lnx → xy(lnx( dy dx) y x) Doing the same, we get that yx(lny x y ( dy dx))




Solve 1 X 2 Dy Dx Y E Tan 1 X



Projecteuclid Org Download Pdf 1 Euclid Chmm
\frac{dy}{dx}=1x^2y^2, Given Here, \frac{dy}{dx} represents the derivative of y with respect to x I will solve for x and y, treating y as a function of x (essentially y=f(x)) \int \frac{dy}{dx}dx=\int 1x^2y^2dxIn mathematics, trigonometric substitution is the substitution of trigonometric functions for other expressions In calculus, trigonometric substitution is a technique for evaluating integralsMoreover, one may use the trigonometric identities to simplify certain integrals containing radical expressions Like other methods of integration by substitution, when evaluating a definite integral, it If y = (tan^–1x)^2 then prove that (1 x^2)^2 d^2y/dx^2 2x(1 x^2) dy/dx = 2 asked in Mathematics by Niharika ( 756k points) differentiation




Engineering Mathematics Notes




Differntials Equatoin
Answer to Find dy/dx y = (1 x2) e tan1x By signing up, you'll get thousands of stepbystep solutions to your homework questions You can Solve the following differential equation (1x^2)dy/dxy=tan^1x askedin Mathematicsby Nisa(597kpoints) differential equations class12 0votes 1answer Let a solution y = y(x) of the differential equation x√(x^2 – 1)dy – y√(y^2 – 1)dx = 0 satisfies y(2) = 2/√3 Assertion (A) y = (x) = sec(sec^1xFind dy/dx tan(xy)=y/(1x^2) Differentiate both sides of the equation Differentiate the left side of the equation Tap for more steps Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that is where and Tap for more steps To apply the Chain Rule, set as The derivative of with respect to is
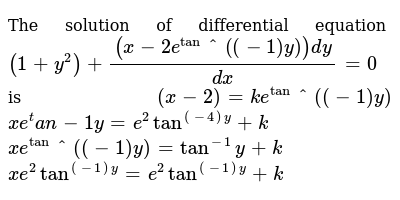



The Solution Of Differential Equation 1 Y 2 X 2e Tan 1 Y




If Y E X Tan Inverse X Prove That D1 X 2 D 2y Dx 2 2 1 X X 2 Dy Dx 1 X 2 Y 0 Maths Application Of Derivatives 1415 Meritnation Com
Given differential equation is (1 x2) dy dx y = etan−1x ( 1 x 2) d y d x y = e t a n − 1 x Therefore, general solution of required differential equation is (ii) becomes It is required solution Please log in or register to add a comment ← Prev Question Next Question →Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and moreIf x 2 x 1 / x 2 2x 1 = A B / (x 1) C / (x 1) 2, then A B = If α, β∈ R are such that 1 – 2i (here i 2 = –1) is a root of z 2 αz β = 0, then (α – β) is equal to If √(1 x 2) √(1 y 2) = a(x y), then dy/dx =




The Solution Of The D E 1 X 2 Dydx Y E Tan 1x Is




Ex 9 6 14 Find Particular Solution 1 X2 Dy Dx 2xy
Get answer Solve (dy),(dx)1=e^(xy) Apne doubts clear karein ab Whatsapp par bhi Try it nowFind the solution of the differential equation that satisfies the given initial conditiondy/dx = y^2 1, y(1) = 0Calculus Find the Derivative d/dx 1/ (tan (x)) 1 tan (x) 1 tan ( x) Rewrite tan(x) tan ( x) in terms of sines and cosines d dx ⎡ ⎢⎣ 1 sin(x) cos(x) ⎤ ⎥⎦ d d x 1 sin ( x) cos ( x) Multiply by the reciprocal of the fraction to divide by sin(x) cos(x) sin ( x) cos ( x) d dx cos(x) sin(x) d d



What Is The Solution For The Differential Equation Math Tan 1 X Y Dx 1 X 2 Dy Math Quora
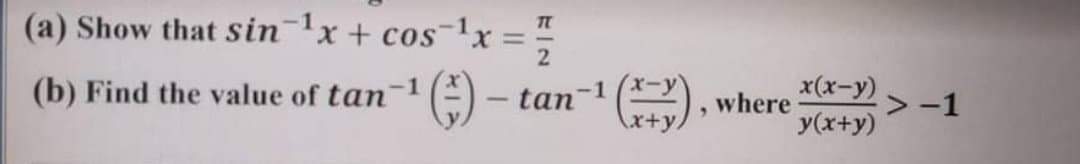



Answered A Show That Sin X Cosx 2 E Bartleby
Get answer (1x^(2))(dy),(dx)y=e^(tan^(1)x) Apne doubts clear karein ab Whatsapp par bhi Try it now
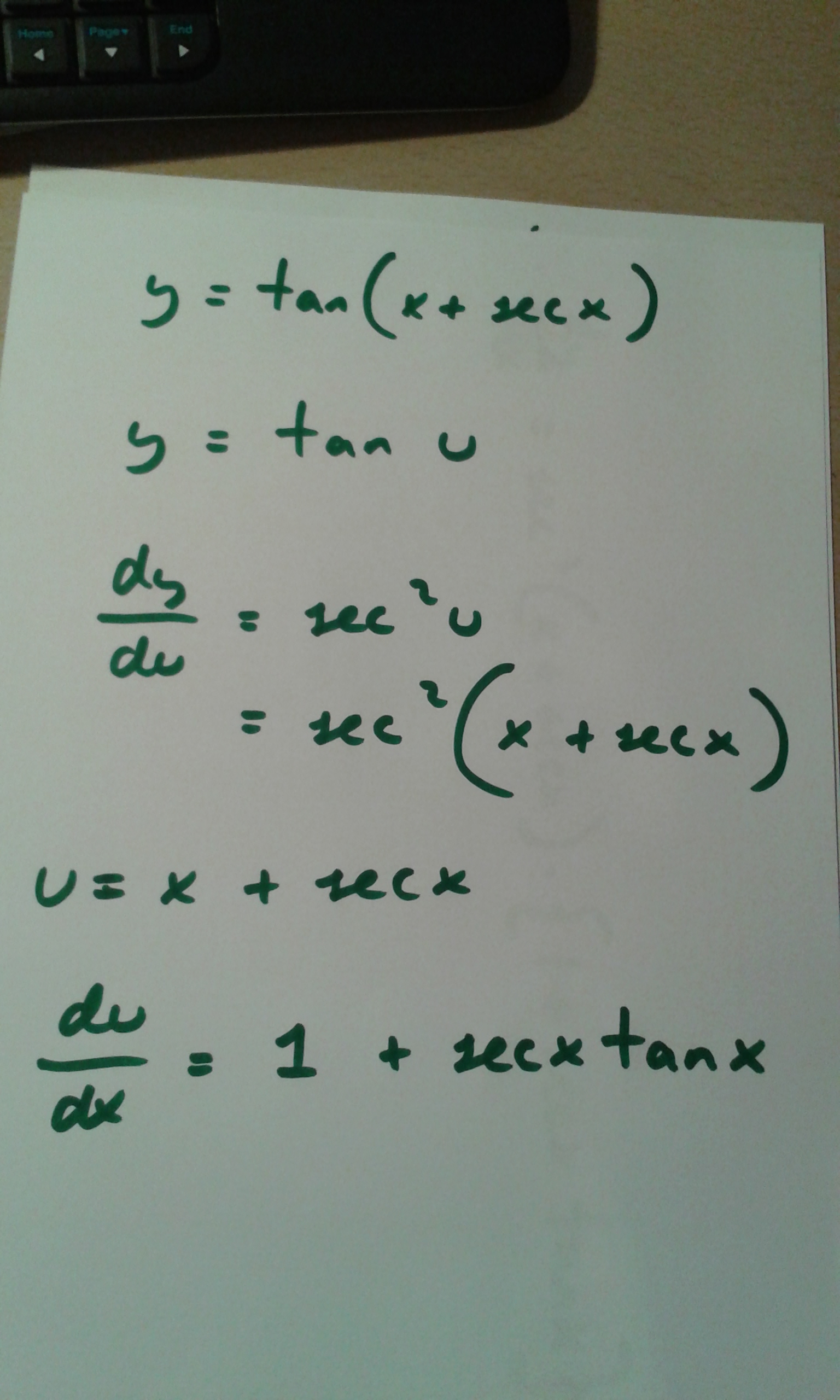



How Do You Find Dy Dx For Y Tan X Sec X Socratic




Solve The Differential Equation Cos 2 X Dy Dx Y Tan X Mathematics And Statistics Shaalaa Com



Find The General Solution Of The Differential Equation 1 Y2 X Etan 1y Dy Dx 0 Studyrankersonline




Solve The Following Des Or Ivps 1 X Cos Y Dx E Chegg Com



What Is The Answer Of Giver Linear Differential Equation Dy Dx Y Tan X E X Quora



Http Www Maths Usyd Edu Au Math1003 R M1003 Coursenotes Sol Pdf




Solve 1 X 2 Dy Dx Y E Tan 1 X




Find Dy Dx For Y E X Tan X Study Com
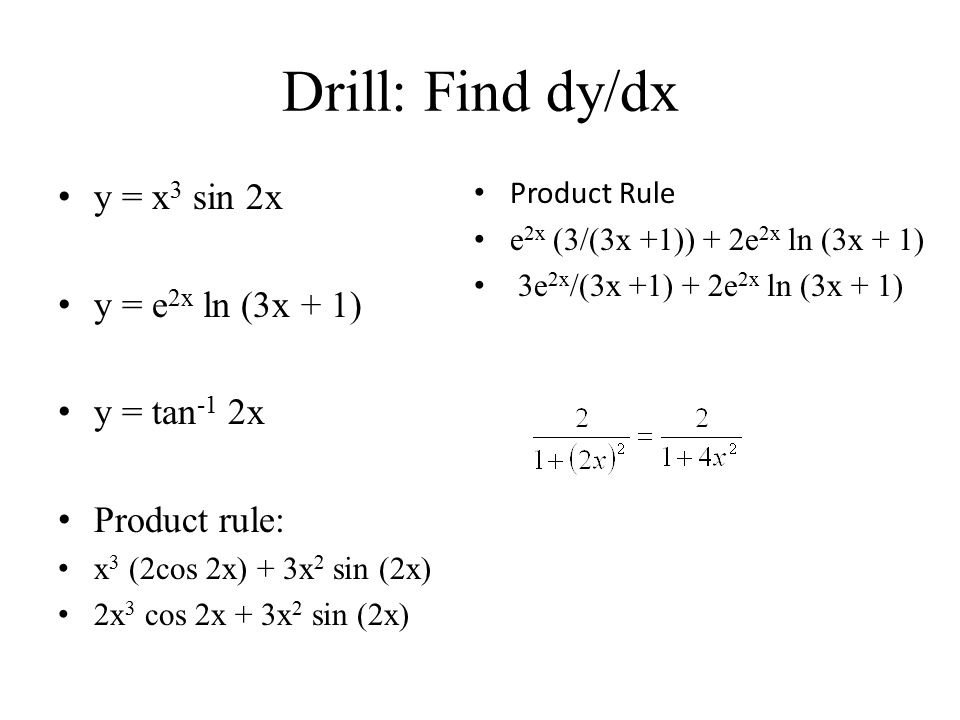



Drill Find Dy Dx Y X 3 Sin 2x Y E 2x Ln 3x 1 Y Tan 1 2x Product Rule X 3 2cos 2x 3x 2 Sin




Solve The Differential Equation Dydx Y Tan X Sin X




Dy Dx Y 2 Novocom Top



Http Www Math Sci Hokudai Ac Jp S Settepanella Teachingfile Calculus Calculus2 Pagine Lineintex Pdf



Secure Media Collegeboard Org Digitalservices Pdf Ap Ap16 Calculus Ab Q4 Pdf




If Y E X Tanx X Log E X Then Find Dy Dx Youtube




Rd Sharma Class 12 Maths Solutions Chapter 11 Differentiation



Http Maths Dur Ac Uk Users Daniel Evans Mes Messolutionsupdated Pdf



Http Www Dunblanehighschool Org Uk Maths Wp Content Uploads 16 03 Differential Equations Pdf




Linear Differential Equations Of First Order Solved Example Problems With Answer Solution Formula




Chain Rule




Ex 9 6 5 Find General Solution Cos2 X Dy Dx Y Tan X




1 X 2 Dy Dx Y Tan 1x Brainly In
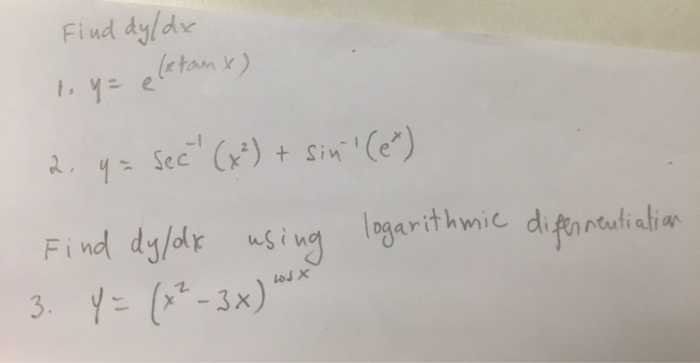



Find Dy Dx Y E X Tanx Y Sec 1 X 2 Chegg Com



Www Tau Ac Il Levant Ode Solution 6 Pdf




If Y E Msin 1 X Prove That 1 X 2 D 2y Dx 2 X Dy Dx M 2y Youtube




If Y E X Tan 1 X Then Prove That Left 1 X 2 Right Frac D 2 Y D X 2 2 Left 1 X X 2 Right Frac D Y D X 1 X 2 Y 0



Secure Media Collegeboard Org Digitalservices Pdf Ap Ap16 Calculus Ab Q4 Pdf
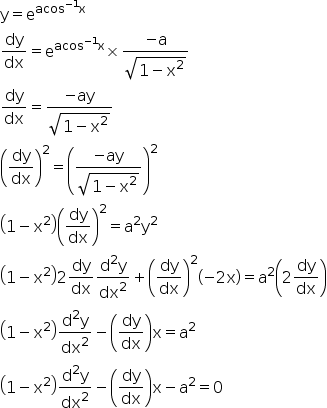



If Y Ea Cos 1 X 1 Mathematics Topperlearning Com Vp7ihcrr
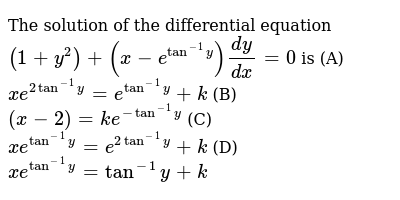



The Solution Of The Differential Equation 1 Y 2 X E Tan 1y



3




What Is The Solution Of Differential Equation D 2y Dx 2 2 Dy Dx Y 0 When X 0 Y 1 Dy Dx 2 Quora



Solve The Differential Equation 1 X 2 Dy Dx Y E Tan 1 X Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



Y E Tan 1x Prove That 1 X 2 Y2 2x 1 Y1 0 In Differential Brainly In



Find Dy Dx If Y Xtanx X2 1 2 Studyrankersonline




Solve 1 X 2 Dy Dx Y E Tan 1x Youtube



Www Ualberta Ca Csproat Homework Math 334 Assignment solutions Assignment 2 solutions Pdf




Ex 9 6 5 Find General Solution Cos2 X Dy Dx Y Tan X



2




Y E Msin 1x Prove That 1 X 2 D 2y Dx 2 Dy Dx M 2y 0 Brainly In




Chapter 04 2500 Solved Problems In Differential Equations Docsity



Www Amherst Edu Media View Original Ma11fall09finalanswers Pdf




Chain Rule




If Y E Tanx Then Dy Dx Is Equal To Brainly In




Solve The Differential Equation Cos 2 X Dy Dx Y Tan X Mathematics And Statistics Shaalaa Com




Ex 9 6 5 Find General Solution Cos2 X Dy Dx Y Tan X



Www Stewartcalculus Com Data Calculus concepts and contexts Upfiles 3c3 Strategy Integra Stu Pdf



1




Engineering Mathematics Notes




If Y Tan 1 Sec X Tan X Then Dy Dx Is Equal To Youtube



Http Www Math Ualberta Ca Xinweiyu 334 1 11f 334 1 11 Hw2 Sol Pdf




8 If Ydfracsin 1xsqrt1 X2 Sho See How To Solve It At Qanda



2



Solve The Differential Equation 1 X 2 Dy Dx Y E Tan 1 X Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




If Y Ex Tan 1 X Prove That 1 X2 D2y Dx2 2 1 X X2 Dy Dx 1 X 2 Y 0 Maths Continuity And Differentiability Meritnation Com



Www Tamdistrict Org Cms Lib Ca Centricity Domain 3 12 Exam Solutions with detailed solutions Pdf




Solution Of The Differential Equation 1 Y 2 X E Tan 1 Y Dy Dx 0 Youtube



Http Concordia Ab Ca Wp Content Uploads 19 09 Apex Infinitesimal Calculus Volume Ii 2 01 Pdf



Www Ucl Ac Uk Zcahge7 Files Week7 Pdf



Pdf Complete Solutions Differential Equations With Modeling Applications Differential Equations With Boundary Value Problems 5th Edition Juan Carlos Becerra Linares Academia Edu




If Y E Tan 1x Find Dy Dx Maths Continuity And Differentiability Meritnation Com




Mp Board Class 12th Maths Important Questions Chapter 9 Differential Equations Mp Board Solutions




Gseb Solutions Class 12 Maths Chapter 9 Differential Equations Ex 9 6 Gseb Solutions
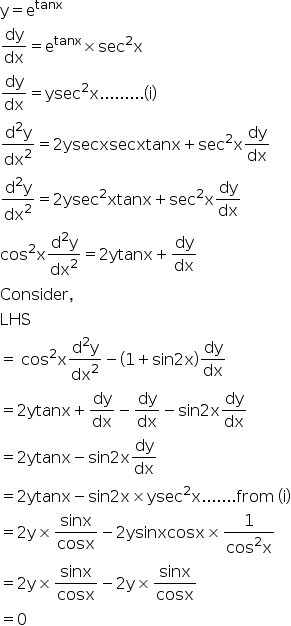



If Y Etan X Prove That Cos2 X D2y Dx2 1 Sin 2x Dy Dx 0 Explain In Great Detail Mathematics Topperlearning Com Mbti5k33




Integral Factor Of 1 X 2 Dy Dx Y E Tan 1x



Ordinary Differential Equations



8 T I Echniques Of



Mryangteacher Weebly Com Uploads 7 7 0 2 Mc Key Unit 6 Solve Diff Eq Ws 2 Pdf




1 Find The General Solution For Each Of The Chegg Com



Solve The Differential Equation 1 Y2 Tan 1 X Dx 2y 1 X2 Dy 0 Studyrankersonline




7 Inverse Functions Inverse Functions 7 3 The



Cdn1 Coolgyan Org Wp Content Uploads 04 Ncert Exemplar Sol Class 12 Mathematics Ch 9 Pdf




Worked Example Implicit Differentiation Video Khan Academy



1



If Y E Tan 1x Show That X 2 1 D 2y Dx 2 2x 1 Dy Dx 0 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



What Is The Answer To Dy Dx For X E T 2 And Y Tan 1 2t 1 Quora




D 2y Dx 2 Dy Dx Y 0 Novocom Top




3 31 Class Work 4 Ye In X E D Y Tanx Y Homeworklib



Solve 1 X 2 Dy Dx Y E Tan 1 X Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



Differential Equations



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿